Ultimate Guide To Different Types of Light Bulbs
Below we provide a detailed explanation of the different types of light bulbs:
- LED light bulbs
- Halogen light bulbs
- Incandescent light bulbs
- Edison light bulbs
- Compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs)
- High-intensity discharge (HID) light bulbs
- Smart light bulbs
- Tungsten light bulbs
- Neon light bulbs
- Induction light bulbs
- Photoluminescent light bulbs
- Carbon filament light bulbs
- Carbon arc light bulbs
LED Light Bulbs
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode. LED light bulbs are a type of energy-efficient lighting technology that use semiconductor materials to produce light. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which produce light by heating a wire filament until it glows, LED bulbs convert electrical energy directly into light, using much less energy in the process.
LED bulbs work by passing a current through a semiconductor material, which causes electrons to release energy in the form of light. The color of the light is determined by the materials used in the semiconductor and the amount of current passed through it.
Compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, LED bulbs are much more energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan. They use up to 90% less energy to produce the same amount of light as an incandescent bulb, which can result in significant cost savings over time. They also produce very little heat, making them safer and more versatile than other types of bulbs.
LED bulbs are available in a wide range of colors and styles, and can be used in a variety of lighting applications, from household lighting to streetlights and even electronic devices like smartphones and televisions.
Advantages:
- Highly energy-efficient: LED bulbs use up to 90% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, which can result in significant cost savings over time.
- Long lifespan: LED bulbs can last up to 25 times longer than incandescent bulbs, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Low heat output: LED bulbs produce very little heat, which can reduce the risk of fires and make them safer to use.
- Instant lighting: LED bulbs turn on instantly with no warm-up time, unlike some other types of bulbs.
- Directional lighting: LED bulbs emit light in a specific direction, which can reduce the need for reflectors and diffusers.
- Flexible design options: LED bulbs can be made in a variety of shapes and sizes, allowing for greater design flexibility.
- Durable: LED bulbs are more durable than traditional bulbs, as they are less susceptible to damage from shocks and vibrations.
- No hazardous materials: LED bulbs do not contain hazardous materials, such as mercury, which can be harmful to the environment.
- Low UV emissions: LED bulbs emit very little ultraviolet (UV) radiation, making them safer for use in areas where UV-sensitive materials are present.
- Wide color range: LED bulbs can produce a wide range of colors, including white light in a variety of color temperatures.
- Dimmable: Some LED bulbs are dimmable, allowing for greater control over the level of light output.
- Reduced cooling costs: As LED bulbs produce less heat, there may be a reduced need for air conditioning, resulting in lower cooling costs.
- Environmentally friendly: LED bulbs use less energy, produce less waste heat, and do not contain hazardous materials, making them a more environmentally friendly lighting choice.
- Cost-effective: While LED bulbs may have a higher upfront cost, their energy efficiency and long lifespan can result in significant cost savings over time.
- Suitable for a variety of applications: LED bulbs can be used for a wide range of lighting applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial lighting.
Disadvantages:
- Higher upfront cost than traditional incandescent bulbs
- Some cheaper LED bulbs may have a lower color rendering index (CRI) which means colors may appear less vibrant or accurate
- LED bulbs may not be compatible with all dimmer switches
- Some people may find the color temperature of LED bulbs to be too cool or blue
- Some LED bulbs may emit electromagnetic interference that can interfere with electronic devices
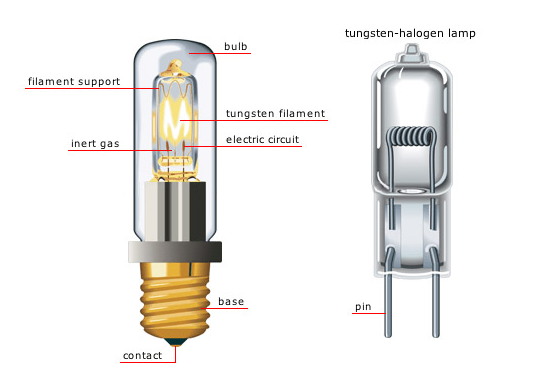
Halogen light bulbs
Halogen light bulbs are a type of incandescent bulb that contain a small amount of halogen gas, such as iodine or bromine, in the bulb. They work by passing an electric current through a filament, which heats up and emits light. The halogen gas in the bulb helps to extend the life of the filament and prevent it from burning out too quickly.
When the filament heats up, it also causes a chemical reaction with the halogen gas, which causes the tungsten from the filament to redeposit onto the filament rather than escaping into the air. This process, called the halogen cycle, helps to keep the filament intact and extend the life of the bulb.
Halogen bulbs are known for their bright, white light and their ability to produce a high level of light output in a small, compact package. They are commonly used in a variety of applications, including household lighting, automotive lighting, and stage lighting.
Advantages:
- Halogen bulbs are relatively inexpensive compared to other types of bulbs, such as LED or CFL bulbs.
- They provide bright, white light that is similar to natural daylight.
- Halogen bulbs are available in a variety of shapes and sizes to fit different fixtures and applications.
- They can be used with dimmer switches to adjust the brightness of the light.
- Halogen bulbs have a high color rendering index (CRI), which means they produce colors that are more accurate and vibrant.
- They have a longer lifespan than traditional incandescent bulbs, typically lasting 2-3 times longer.
- They are easy to install and replace.
- Halogen bulbs produce instant light when turned on, unlike some other types of bulbs that may take a few moments to reach full brightness.
- They are often used in task lighting and accent lighting due to their bright, focused light.
Disadvantages:
- Halogen bulbs are less energy-efficient than LED or CFL bulbs, which means they consume more electricity and cost more to operate over time.
- They produce more heat than other types of bulbs, which can be a safety hazard if they are used in enclosed fixtures or in close proximity to flammable materials.
- Halogen bulbs have a shorter lifespan than LED or CFL bulbs, which means they need to be replaced more frequently.
- They are more fragile than other types of bulbs and can be easily damaged if dropped or bumped.
- Halogen bulbs emit UV radiation, which can be harmful to skin and fabrics if used in close proximity.
- They may not be compatible with certain fixtures or applications, which can limit their versatility.
- They can be expensive to replace if a large number of bulbs are needed, such as in commercial or industrial settings.
- They are not as environmentally friendly as LED or CFL bulbs, as they contain halogen gas and require special disposal methods.
- Halogen bulbs may not be as widely available in the future due to energy efficiency regulations, which are phasing out less efficient lighting options.
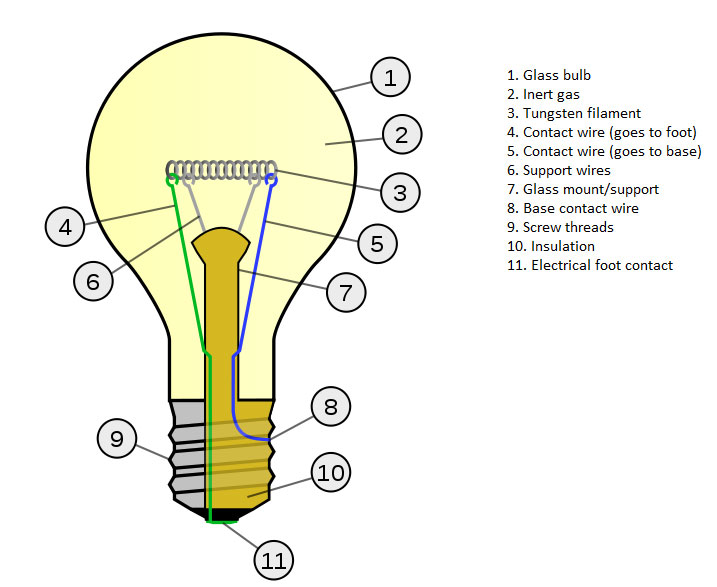
Incandescent light bulbs
Incandescent light bulbs are a type of light bulb that work by passing an electric current through a filament, which heats up and emits light. The filament is usually made of tungsten, which has a high melting point and can withstand the high temperatures required to produce light.
When the electric current passes through the filament, it heats up and becomes so hot that it emits visible light. The filament is contained within a glass bulb that is filled with an inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen, which helps to prevent the filament from burning out too quickly.
As the filament emits light, it also emits heat, which is why incandescent bulbs are less energy-efficient than other types of bulbs. In fact, only about 5-10% of the energy used by an incandescent bulb is converted into visible light, while the rest is wasted as heat.
Incandescent bulbs are known for their warm, yellowish light and their ability to produce a smooth, even glow. They are commonly used in a variety of applications, including household lighting, commercial lighting, and automotive lighting.
Advantages:
- Incandescent bulbs provide warm, yellowish light that is similar to natural daylight.
- They are widely available and can be found at most hardware stores, supermarkets, and convenience stores.
- Incandescent bulbs are relatively inexpensive compared to other types of bulbs, such as LED or CFL bulbs.
- They are easy to install and replace.
- Incandescent bulbs produce instant light when turned on, unlike some other types of bulbs that may take a few moments to reach full brightness.
- They can be used with dimmer switches to adjust the brightness of the light.
- Incandescent bulbs do not contain hazardous materials, such as mercury, which can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly.
- They are compatible with a wide range of fixtures and applications, which makes them versatile and easy to use.
- Incandescent bulbs have a high color rendering index (CRI), which means they produce colors that are more accurate and vibrant.
- They can be used in outdoor settings, as they are not affected by cold temperatures or weather conditions.
Disadvantages:
- Incandescent bulbs are less energy-efficient than other types of bulbs, which means they consume more electricity and cost more to operate over time.
- They have a shorter lifespan than LED or CFL bulbs, which means they need to be replaced more frequently.
- Incandescent bulbs emit more heat than light, which can be a safety hazard if they are used in enclosed fixtures or in close proximity to flammable materials.
- They are not as environmentally friendly as LED or CFL bulbs, as they waste a significant amount of energy as heat and require more energy to operate.
- Incandescent bulbs are becoming less common due to energy efficiency regulations, which are phasing out less efficient lighting options.
- They are not as bright as other types of bulbs and may not be suitable for applications that require high levels of illumination.
- Incandescent bulbs are not as versatile as other types of bulbs, as they may not be compatible with certain fixtures or applications.
- They can be expensive to operate over time, as their energy consumption can significantly increase electricity bills.
- Incandescent bulbs may produce a yellowish or orange glow, which may not be ideal for certain applications, such as reading or task lighting.
Edison light bulbs
Edison light bulbs are a type of incandescent light bulb that were first invented by Thomas Edison in the late 19th century. These bulbs work on the same principle as other incandescent bulbs, with a filament that is heated to produce light.
The filament in an Edison bulb is made of carbonized bamboo or other materials, which is enclosed in a vacuum-sealed glass bulb. The vacuum-sealed environment prevents the filament from burning out too quickly by reducing the amount of oxygen in the bulb.
When an electric current is passed through the filament, it heats up and emits light. The filament glows as it heats up, producing a warm, yellowish light that is similar to candlelight.
Edison bulbs were once very popular and are still used in some decorative lighting applications today, although they are less common than other types of bulbs. They are known for their unique and vintage aesthetic, and are often used in antique or retro-themed designs.
Advantages:
- Edison bulbs have a unique and vintage aesthetic that adds character and charm to any space.
- They provide a warm, yellowish light that is similar to candlelight and creates a cozy atmosphere.
- Edison bulbs are available in a variety of shapes and sizes, which makes them versatile and adaptable to different lighting fixtures and applications.
- They are relatively easy to install and replace.
- Edison bulbs can be used with dimmer switches to adjust the brightness of the light.
- They are compatible with a wide range of fixtures and applications, which makes them versatile and easy to use.
- Edison bulbs do not contain hazardous materials, such as mercury, which can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly.
- They can be used in outdoor settings, as they are not affected by cold temperatures or weather conditions.
- Edison bulbs have a high color rendering index (CRI), which means they produce colors that are more accurate and vibrant.
- They are known for their long lifespan and durability, which means they do not need to be replaced as frequently as other types of bulbs.
Disadvantages:
- Edison bulbs are less energy-efficient than other types of bulbs, which means they consume more electricity and cost more to operate over time.
- They emit more heat than light, which can be a safety hazard if they are used in enclosed fixtures or in close proximity to flammable materials.
- Edison bulbs have a shorter lifespan than LED or CFL bulbs, which means they need to be replaced more frequently.
- They are not as environmentally friendly as LED or CFL bulbs, as they waste a significant amount of energy as heat and require more energy to operate.
- Edison bulbs are becoming less common due to energy efficiency regulations, which are phasing out less efficient lighting options.
- They are not as bright as other types of bulbs and may not be suitable for applications that require high levels of illumination.
- Edison bulbs are not as versatile as other types of bulbs, as they may not be compatible with certain fixtures or applications.
- They can be expensive to operate over time, as their energy consumption can significantly increase electricity bills.
- Edison bulbs may produce a yellowish or orange glow, which may not be ideal for certain applications, such as reading or task lighting.
- They can be fragile and may break easily if not handled carefully.
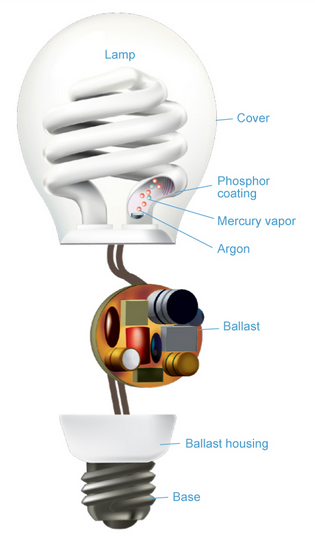
Compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs)
Compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs) are a type of energy-efficient lighting that work in a similar way to traditional fluorescent bulbs but are designed to fit into standard light fixtures. They were developed as a more efficient replacement for incandescent bulbs and have become increasingly popular in recent years.
Here's how they work:
- A CFL bulb is a small, twisted tube that contains a small amount of mercury vapor and an inert gas, such as argon or krypton.
- The tube is coated with a phosphor powder, which absorbs the ultraviolet radiation produced by the mercury vapor when it is excited by an electrical current.
- When electricity is supplied to the bulb, an electrical charge flows through the gas and vapor, which causes the mercury atoms to release ultraviolet light.
- The ultraviolet light is then absorbed by the phosphor coating, which causes it to emit visible light.
- The resulting light is much brighter and more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs, as it uses much less energy to produce the same amount of light.
CFL bulbs are designed to fit into standard light fixtures, making them a convenient and easy-to-use option for residential and commercial applications. They are available in a range of shapes and sizes, including spiral, globe, and reflector bulbs, and can be used for a variety of applications, such as general lighting, task lighting, and outdoor lighting.
There are some key differences between fluorescent light bulbs and compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs):
- Shape and Size: Fluorescent bulbs are typically long, tubular bulbs that are commonly used in ceiling fixtures, whereas CFLs can be found in a variety of shapes and sizes, including spiral and globe-shaped bulbs that can be used in lamps and other fixtures.
- Energy Efficiency: CFLs are more energy-efficient than fluorescent bulbs. They use about 75% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and last up to 10 times longer than incandescent bulbs.
- Brightness: CFLs are generally brighter than fluorescent bulbs.
- Warm-up Time: Fluorescent bulbs typically require a warm-up time of a few seconds before reaching their full brightness, while CFLs usually reach full brightness almost instantly.
- Cost: CFLs are more expensive than fluorescent bulbs, but their longer lifespan and energy efficiency mean that they can save you money in the long run.
- Disposal: CFLs contain a small amount of mercury, which makes them difficult to dispose of safely. Fluorescent bulbs also contain mercury, but in lower amounts.
- Environmental Impact: CFLs have a lower environmental impact than fluorescent bulbs because they use less energy, emit less greenhouse gas, and produce less waste. However, the mercury in CFLs can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly.
Advantages:
- Energy efficiency: CFLs use up to 75% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, resulting in lower electricity bills and reduced overall demand for energy.
- Cost-effectiveness: Although CFLs have a higher upfront cost than incandescent bulbs, they have a longer lifespan and use less energy, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
- Long lifespan: CFLs can last up to 10 times longer than incandescent bulbs, reducing the frequency of replacement and overall maintenance costs.
- Lower heat emission: CFLs emit less heat than incandescent bulbs, reducing the risk of fire and making them a safer lighting option, particularly in enclosed spaces.
- Range of brightness levels: CFLs are available in a range of brightness levels, from warm to cool light, making them suitable for different lighting needs and preferences.
- Instant start-up: CFLs reach their full brightness almost instantly, making them a convenient lighting option, particularly in areas where frequent switching on and off is required.
- Range of color temperatures: CFLs are available in a range of color temperatures, including warm white, cool white, and daylight, providing a variety of options for different applications.
- Easy to install: CFLs are easy to install and can be used in a variety of fixtures, including table lamps, ceiling fixtures, and recessed lighting.
- Improved lighting quality: CFLs provide a more consistent and uniform light distribution than incandescent bulbs, resulting in improved lighting quality.
- Reduced environmental impact: CFLs use less energy and have a longer lifespan than incandescent bulbs, resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions, lower carbon footprint, and reduced environmental impact.
- Lower mercury content: While CFLs do contain small amounts of mercury, the amount is lower than in older fluorescent bulbs, and CFLs can be safely disposed of through recycling programs.
- Greater durability: CFLs are more durable than incandescent bulbs, making them less prone to breakage and damage.
- Lower maintenance cost: Due to their longer lifespan, CFLs require less frequent replacement, resulting in lower maintenance costs.
- No flickering: CFLs produce steady and flicker-free light, reducing eye strain and discomfort for those using them.
Disadvantages:
- Higher upfront cost: CFLs have a higher upfront cost than traditional incandescent bulbs, which can be a deterrent for some consumers.
- Mercury content: While the mercury content in CFLs is relatively low, it can still pose a risk to the environment if not disposed of properly. CFLs should be disposed of through recycling programs to ensure proper handling of the mercury.
- Dimming limitations: CFLs can be difficult to dim or may not be compatible with some dimmer switches, which can be inconvenient for some users.
- Warm-up time: Although CFLs reach their full brightness almost instantly, they may take some time to warm up and reach their full brightness in cold temperatures.
- Disposal challenges: Disposing of CFLs can be more challenging than traditional incandescent bulbs due to their mercury content, which can make them difficult to recycle or dispose of properly.
- Limited temperature range: CFLs may not perform well in extreme temperatures, such as very hot or very cold environments.
- Compatibility issues: CFLs may not be compatible with all types of fixtures, particularly those designed for incandescent bulbs.
- Potential for flickering: Some CFLs may flicker or produce inconsistent light, which can be uncomfortable for some users.
- UV radiation: CFLs can emit low levels of UV radiation, which can be harmful to people and materials in close proximity to the bulb over time.
- Not suitable for all applications: CFLs may not be suitable for all lighting applications, particularly those that require instant and consistent light, such as some photography and videography settings.
High-intensity discharge (HID) light bulbs
High-intensity discharge (HID) light bulbs are a type of lighting technology that produces very bright light using an electrical charge. These bulbs are commonly used in streetlights, stadiums, and other large outdoor areas where powerful lighting is required.
HID bulbs work by passing an electric current through a gas-filled chamber. This gas is typically a mixture of metal halides, such as mercury, sodium, or metal iodides. When the current flows through the gas, it ionizes the gas, creating a plasma. This plasma emits ultraviolet (UV) light.
The UV light then hits a phosphor coating on the inside of the bulb, which converts the UV light into visible light. The color temperature and the intensity of the light depend on the type of metal halide used in the bulb.
HID bulbs are known for their high efficiency and long lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. However, they do require a ballast to regulate the electrical current flowing through the bulb, and they can take a few seconds to reach full brightness after being turned on.
Advantages:
- Brightness: HID bulbs produce very bright light, making them suitable for lighting large areas such as parking lots, sports arenas, and highways.
- Efficiency: HID bulbs are much more efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs. They produce more light per watt of energy used, which can result in lower energy bills and reduced carbon emissions.
- Long lifespan: HID bulbs have a longer lifespan than incandescent bulbs, which means they need to be replaced less often. This can result in cost savings over time, especially in areas where lighting is used frequently.
- Color temperature: HID bulbs come in a range of color temperatures, from warm yellow to cool blue-white. This allows them to be customized to suit different applications and aesthetics.
- Durability: HID bulbs are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures and vibrations. This makes them ideal for outdoor and industrial applications.
- Wide coverage area: HID bulbs can provide a wider coverage area than other types of lighting, which can reduce the number of fixtures needed to light a large space.
- Improved visibility: HID bulbs provide clearer and more natural-looking light than other types of lighting, which can improve visibility and safety in certain applications.
- Versatility: HID bulbs can be used for a wide range of applications, from street lighting and stadium lighting to automotive headlights and stage lighting.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: HID bulbs can be more expensive than other types of lighting, such as incandescent or LED bulbs. Additionally, they require a ballast to regulate the electrical current, which can add to the cost.
- Warm-up time: HID bulbs can take a few seconds to reach full brightness after being turned on. This can be an issue in situations where instant brightness is required.
- Glare: HID bulbs can produce a lot of glare, especially when used in applications such as headlights or street lighting. This can be a safety hazard for drivers and pedestrians.
- UV radiation: HID bulbs produce UV radiation, which can be harmful to human skin and eyes. This is typically not an issue in outdoor applications, but it can be a concern in indoor settings.
- Color shift: HID bulbs can shift in color over time, becoming less bright and less consistent in their color temperature. This can require frequent replacements to maintain consistent lighting.
- Maintenance: HID bulbs require periodic maintenance, such as cleaning and replacement of the ballast. This can add to the cost and complexity of using HID lighting.
- Environmental impact: HID bulbs contain hazardous materials, such as mercury and metal halides, which can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly. Additionally, HID bulbs consume more energy than other types of lighting, which can contribute to carbon emissions and other environmental issues.
Smart light bulbs
Smart light bulbs are a type of LED bulb that can be controlled wirelessly using a smartphone, tablet, or other smart device. They are part of a larger category of products known as smart home technology, which allows users to automate and control various aspects of their home environment using technology.
Smart light bulbs typically connect to a home's Wi-Fi network and are controlled using a mobile app. Users can turn the lights on or off, adjust the brightness, and even change the color temperature or color of the light.
Many smart light bulbs also have additional features, such as the ability to schedule lighting changes, integrate with other smart home devices such as voice assistants or motion sensors, and even respond to music or other audio cues.
Smart light bulbs work by incorporating a small computer chip and wireless connectivity into the bulb itself. This chip allows the bulb to communicate with other devices on the home network and receive commands from a mobile app or other source.
In addition to their convenience and flexibility, smart light bulbs are also known for their energy efficiency. They use LED technology, which consumes less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, and they can be programmed to turn off or dim automatically when not in use.
Advantages:
- Control: With smart light bulbs, you have complete control over your lighting. You can turn lights on or off, adjust brightness, and change the color temperature or color of the light from your phone or other smart device, even when you're not at home.
- Convenience: Smart light bulbs offer a high level of convenience, especially when it comes to scheduling and automation. You can program your lights to turn on or off at specific times, or in response to other triggers, such as motion sensors or voice commands.
- Energy efficiency: Smart light bulbs use LED technology, which consumes less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs. They can also be programmed to turn off or dim automatically when not in use, helping to reduce energy waste.
- Customization: Smart light bulbs offer a high degree of customization, allowing you to tailor the lighting in your home to suit different moods and activities. You can adjust the brightness and color temperature to create a cozy atmosphere for movie night or a bright, energizing light for a workout.
- Integration: Smart light bulbs can integrate with other smart home devices, such as voice assistants, smart thermostats, and security systems, to create a seamless and interconnected home environment.
- Cost-effective: Smart light bulbs may be more expensive than traditional bulbs, but they can be cost-effective in the long run. With energy savings and reduced bulb replacements, you may save money over time.
- Security: Smart light bulbs can be used to enhance home security by making it appear as though someone is home, even when you're away. You can program your lights to turn on and off at random intervals, making it more difficult for potential intruders to target your home.
- Accessibility: Smart light bulbs can be especially beneficial for people with mobility issues or disabilities, as they can be controlled using a smartphone or other device without the need to physically manipulate a light switch.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: Smart light bulbs can be more expensive than traditional light bulbs, and they also require a compatible smart device, such as a smartphone or tablet, to control them.
- Wi-Fi connectivity: Smart light bulbs rely on Wi-Fi connectivity to communicate with other devices, and this can be a problem in areas with poor network coverage. Additionally, if your home network goes down, you may lose control of your smart bulbs.
- Complexity: Smart light bulbs can be more complex to set up and use than traditional bulbs, and some users may find the process of connecting and configuring the bulbs to be frustrating.
- Compatibility issues: Smart light bulbs may not be compatible with all smart home devices, and you may need to purchase additional equipment or use a specific app to control your lights.
- Security risks: Smart light bulbs may pose a security risk if they are not properly secured. Hackers can potentially gain access to your home network through a vulnerable smart bulb, putting your personal data and privacy at risk.
- Limited availability: Smart light bulbs are still relatively new on the market, and they may not be widely available in all areas. This can make it difficult to find the bulbs you need, or to get help if you encounter problems with your setup.
- Reliability: Like all technology, smart light bulbs can sometimes fail or malfunction, leaving you without control over your lighting until the problem is resolved. Additionally, if the mobile app or other controlling device malfunctions, you may be unable to control your lights until the issue is resolved.
Tungsten light bulbs
Tungsten light bulbs are a type of incandescent light bulb that uses a tungsten filament to produce light. The bulb contains a wire filament made of tungsten, which is a very strong and heat-resistant metal. When an electric current passes through the filament, it heats up and begins to emit light.
The process by which tungsten light bulbs work is called incandescence. When an electric current passes through a material, it heats up the atoms and causes them to emit light. In the case of tungsten light bulbs, the filament is heated to a very high temperature, typically around 2,500 degrees Celsius. At this temperature, the tungsten filament begins to glow and emit light.
Tungsten light bulbs are known for their warm and cozy glow, and are often used in homes and businesses for general lighting purposes. They are relatively inexpensive and widely available, making them a popular choice for many applications.
Advantages:
- Warm and cozy light: Tungsten light bulbs produce a warm and cozy light that is often preferred for creating a comfortable and relaxing atmosphere in homes and businesses.
- Affordable: Tungsten light bulbs are relatively inexpensive and widely available, making them an affordable lighting option for many people.
- Wide range of styles: Tungsten light bulbs are available in a wide range of shapes and sizes, making them suitable for use in a variety of fixtures and applications.
- Instant-on: Tungsten light bulbs turn on instantly when the switch is flipped, which can be a desirable feature in some applications.
- Dimmable: Many tungsten light bulbs are dimmable, which allows users to adjust the brightness of the light to suit their needs.
- Easy to find: Tungsten light bulbs are widely available at hardware stores, home improvement stores, and online retailers, making them easy to find and purchase.
- No special disposal requirements: Tungsten light bulbs do not contain any hazardous materials, so they can be disposed of in the regular trash.
- No flickering: Unlike some other types of bulbs, tungsten light bulbs do not flicker, which can be a desirable feature for some people.
- High color rendering index: Tungsten light bulbs have a high color rendering index (CRI), which means that they accurately reproduce colors in the light they produce. This can be important for applications such as photography and art display.
Disadvantages:
- Low efficiency: Tungsten light bulbs are not very energy-efficient, as the majority of the energy they consume is converted into heat rather than light. This can lead to higher energy costs and increased carbon emissions.
- Short lifespan: Tungsten light bulbs have a relatively short lifespan compared to other types of bulbs, typically around 1,000 hours. This means that they need to be replaced more frequently, which can be inconvenient and costly.
- Fragility: Tungsten filaments are fragile and can break easily if the bulb is bumped or jostled. This can lead to premature failure of the bulb.
- Heat output: Tungsten light bulbs produce a significant amount of heat, which can be a disadvantage in applications where heat buildup is a concern, such as in small enclosed spaces or in hot climates.
- Limited color options: Tungsten light bulbs produce a warm, yellowish light that may not be suitable for all applications. They are not available in a wide range of colors like some other types of bulbs.
- Not compatible with some fixtures: Some fixtures, such as those with built-in dimming controls or electronic ballasts, may not be compatible with tungsten light bulbs. This can limit their usefulness in certain applications.
- Environmental impact: Tungsten light bulbs contain a small amount of mercury, which is a hazardous material that can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly.
Neon light bulbs
Neon light bulbs are a type of gas-discharge lamp that contain a small amount of neon gas, as well as other noble gases such as argon, helium, or krypton. These gases are housed within a glass tube that is sealed at both ends and contains two electrodes.
When a high voltage electrical current is applied to the electrodes, it ionizes the gas atoms, causing them to emit light. The color of the light emitted depends on the type of gas used, as well as the pressure and shape of the tube.
Neon light bulbs can be formed into a variety of shapes and designs, and are often used for decorative lighting, signage, and advertising. They are known for their distinctive bright colors and unique glow, which can create a nostalgic or retro feel.
While neon light bulbs are not as energy efficient as some other types of lighting, they have a long lifespan and are very durable and resistant to shock and vibration. They also emit very little heat, making them a safe option for use in a variety of settings.
Advantages:
- Neon light bulbs are very energy efficient, using only a small amount of electricity to produce a bright and colorful light.
- They have a very long lifespan, often lasting up to 10 times longer than traditional incandescent bulbs.
- They emit very little heat, making them a safer option for use in a variety of settings, such as homes, offices, and public spaces.
- Neon light bulbs are highly customizable and can be shaped into a wide range of designs and patterns, making them ideal for use in artistic installations or signage.
- They are extremely durable and resistant to shock and vibration, making them suitable for use in harsh environments and outdoor settings.
- Neon lights are often more visually appealing than other types of lighting, due to their bright and vibrant colors and unique glow.
- They are relatively easy to install and maintain, requiring minimal upkeep and replacement over time.
- Neon light bulbs are environmentally friendly, as they contain no harmful chemicals and are fully recyclable.
- They are a popular choice for use in retro or vintage-inspired decor, adding a touch of nostalgia to any space.
- They can be used for a variety of applications, including advertising, decorative lighting, and art installations.
Disadvantages:
- Neon light bulbs can be relatively expensive compared to other types of lighting, especially for custom designs or installations.
- They require a high voltage power supply to operate, which can pose a risk of electric shock or fire if not installed properly.
- Neon lights are not as energy efficient as some other types of lighting, such as LED or fluorescent bulbs.
- They can be fragile and easily damaged, especially during transportation or installation.
- Neon lights are not suitable for use in areas with extreme temperatures, as they can become dimmer or stop working altogether in very hot or cold conditions.
- They are not as versatile as some other types of lighting, as they are limited in the range of colors and designs they can produce.
- Neon lights can be difficult to repair if they are damaged or broken, requiring specialized knowledge and tools.
- They may require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and brightness over time.
- They can produce a buzzing or humming sound when in use, which can be distracting or irritating in quiet environments.
- Neon lights can be less effective for illuminating large areas, as they have a focused, directional beam of light rather than a diffuse, spread-out glow.
Induction light bulbs
Induction light bulbs are a type of high-efficiency lighting that uses electromagnetic induction to produce light. They consist of a sealed glass bulb containing a gas mixture, a high-frequency generator, and a magnetic coil.
When electricity is supplied to the magnetic coil, it produces a high-frequency electromagnetic field that ionizes the gas mixture in the bulb. This ionization process creates ultraviolet light, which is not visible to the human eye.
The ultraviolet light then strikes a phosphor coating on the inside of the glass bulb, causing it to emit visible light. This process is similar to the way fluorescent bulbs work, but induction bulbs use a magnetic field to ionize the gas mixture instead of a direct electrical current.
Induction bulbs are known for their energy efficiency and long lifespan, with some models lasting up to 100,000 hours or more. They also emit very little heat and have a high color rendering index, making them suitable for use in a variety of settings, such as parking lots, roadways, and commercial buildings.
One disadvantage of induction bulbs is their high initial cost compared to traditional bulbs, but they are often considered a cost-effective option over the long-term due to their energy efficiency and longevity.
Advantages:
- Induction light bulbs have a very long lifespan, often lasting up to 100,000 hours or more, which reduces the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
- They are highly energy efficient, using up to 70% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, which can significantly reduce energy costs.
- They emit very little heat, making them a safe option for use in a variety of settings, including public spaces, commercial buildings, and industrial environments.
- Induction bulbs have a high color rendering index (CRI), which means they accurately reproduce colors and make objects appear more vibrant and natural.
- They have a fast startup time, reaching full brightness almost instantly when turned on, which is particularly useful in environments where quick lighting is required, such as parking lots or industrial settings.
- Induction bulbs have a low lumen depreciation rate, which means they maintain their brightness and light output over time, even with extended use.
- They are environmentally friendly, containing no hazardous materials such as mercury, and are fully recyclable.
- Induction light bulbs are resistant to shock and vibration, making them suitable for use in harsh or rugged environments, such as outdoor lighting or industrial settings.
- They can be used in a wide range of applications, including street lighting, parking lot lighting, stadium lighting, and commercial building lighting.
- Induction bulbs are generally considered to be a cost-effective lighting solution over the long term, despite their higher initial cost.
Disadvantages:
- High initial cost: Induction bulbs are more expensive to purchase than traditional incandescent bulbs or even LED bulbs.
- Limited availability: Induction bulbs are not as widely available as other types of bulbs, making it difficult to find replacements or spare parts.
- Limited brightness options: Induction bulbs are typically not as bright as other types of bulbs, limiting their use in certain applications.
- Limited color options: Induction bulbs typically only come in a limited range of color temperatures, making it difficult to achieve certain lighting effects.
- Not dimmable: Induction bulbs are generally not compatible with dimmer switches, which can limit their use in certain applications.
- Fragility: Induction bulbs are relatively fragile and can be easily damaged if dropped or mishandled.
- Heavy weight: Induction bulbs are often heavier than other types of bulbs, which can make them difficult to install or maneuver.
- Limited lifespan: Induction bulbs have a limited lifespan, typically lasting between 60,000 and 100,000 hours, which is less than the lifespan of LED bulbs.
- Environmental concerns: Induction bulbs contain small amounts of mercury, which can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly.
Photoluminescent light bulbs
Photoluminescent light bulbs, also known as glow-in-the-dark light bulbs, are a type of lighting technology that uses phosphorescent materials to emit light without the need for electricity.
These bulbs work by absorbing and storing energy from ambient light or other light sources, such as incandescent or LED bulbs. The phosphorescent material inside the bulb then emits this stored energy as a soft glow, even after the light source has been turned off.
The technology behind photoluminescent light bulbs is based on the principle of photoluminescence, which is the emission of light from a material after it has absorbed light. In the case of these light bulbs, the phosphorescent material is typically a type of rare earth element or a mixture of phosphors that are designed to emit light in a specific color or wavelength.
Photoluminescent light bulbs are often used in emergency lighting applications, as they do not require a power source and can continue to emit light for several hours after the power has been cut. They can also be used as decorative lighting, as they can add a unique and ambient glow to a room or space.
Advantages:
- Energy-efficient: Photoluminescent light bulbs do not require electricity to operate, which makes them highly energy-efficient and cost-effective.
- Environmentally friendly: Because photoluminescent light bulbs do not require electricity, they do not contribute to greenhouse gas emissions or other harmful pollutants.
- Long-lasting: Photoluminescent light bulbs can continue to emit light for several hours after being exposed to a light source, making them a reliable and long-lasting source of illumination.
- Low maintenance: Because they do not have any moving parts or require any electrical components, photoluminescent light bulbs are very low maintenance and do not require frequent replacement.
- Safe: Photoluminescent light bulbs do not generate any heat or emit any UV radiation, making them safe to use in a variety of settings, including in areas where flammable or hazardous materials are present.
- Easy to install: Photoluminescent light bulbs are easy to install and can be used in a variety of settings, including in emergency lighting applications or as decorative lighting.
- Versatile: Photoluminescent light bulbs can be used in a variety of settings, including in homes, offices, and public spaces, and can be customized to emit light in different colors or wavelengths.
- Reliable: Photoluminescent light bulbs are highly reliable and can continue to emit light even in the event of a power outage or other emergency situation.
- Cost-effective: Because they do not require electricity to operate, photoluminescent light bulbs can be a cost-effective alternative to traditional lighting solutions.
Disadvantages:
- Limited brightness: Photoluminescent light bulbs are typically not as bright as other types of light bulbs, which can limit their use in certain applications.
- Limited color options: The color of the light emitted by photoluminescent light bulbs is typically limited to a specific range, which may not be suitable for all lighting applications.
- Limited duration of illumination: The duration of illumination provided by photoluminescent light bulbs depends on the amount of energy they absorb from light sources, which may not be sufficient for all lighting needs.
- Limited range of use: Photoluminescent light bulbs are primarily designed for emergency lighting applications, and may not be suitable for use in all lighting situations.
- Limited availability: Photoluminescent light bulbs may not be as widely available as other types of light bulbs, which can make it difficult to find replacement bulbs or spare parts.
- Maintenance requirements: Although photoluminescent light bulbs do not require electricity to operate, they do require periodic exposure to light in order to maintain their level of illumination.
- Fragility: Photoluminescent light bulbs are relatively fragile and can be easily damaged if dropped or mishandled.
- Initial cost: The cost of photoluminescent light bulbs may be higher than that of other types of light bulbs, due to the cost of the rare earth elements and other materials used in their production.
- Limited customization options: The design and customization options for photoluminescent light bulbs may be limited compared to other types of light bulbs, which may make it difficult to achieve certain lighting effects.
Carbon filament light bulbs
Carbon filament light bulbs are a type of incandescent light bulb that uses a carbon filament to produce light. These bulbs were first developed in the late 1800s and were widely used in homes and businesses until the 1920s, when they were largely replaced by more efficient types of bulbs.
The carbon filament in a carbon filament bulb is made by heating a strand of carbonized bamboo or other plant material until it becomes charred and black. The resulting filament is then wound into a coil and placed inside a glass bulb that is filled with an inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon, to prevent the filament from burning up.
When an electric current is passed through the filament, it heats up and begins to glow, producing light. The color of the light produced by a carbon filament bulb is determined by the temperature of the filament. At lower temperatures, the light is more orange or yellow, while at higher temperatures it is more white or blue.
Carbon filament bulbs are known for their warm, amber-colored light, which is often associated with vintage and Edison-style bulbs. However, they are not very energy-efficient and have a relatively short lifespan compared to other types of bulbs, which has led to their decline in popularity in recent years.
Advantages:
- Warm, amber-colored light: Carbon filament bulbs produce a warm, yellow-orange light that is often preferred for creating a cozy, vintage ambiance in homes, restaurants, and other settings.
- Aesthetic appeal: Carbon filament bulbs are available in a wide variety of shapes and sizes, and their unique filament designs can add an artistic or decorative touch to a room.
- Easy to dim: Carbon filament bulbs are typically compatible with dimmer switches, which allows for greater control over the brightness and ambiance of a room.
- Instant light: Carbon filament bulbs light up immediately when turned on, without the need for warm-up time.
- Low cost: Carbon filament bulbs can be relatively inexpensive compared to other types of bulbs, making them an affordable choice for decorative lighting applications.
- Compatibility: Carbon filament bulbs are often designed to be compatible with traditional light fixtures, which means that they can be easily integrated into existing lighting systems.
- High color rendering index (CRI): Carbon filament bulbs typically have a high CRI, which means that they are able to accurately reproduce colors in a way that is pleasing to the eye.
- Low blue light emissions: Carbon filament bulbs emit very little blue light, which can help to reduce eye strain and promote better sleep in the evening.
- Environmental friendliness: Carbon filament bulbs do not contain any hazardous materials, such as mercury, and can be safely disposed of in the regular trash.
Disadvantages:
- Low efficiency: Carbon filament bulbs are not very energy-efficient, as they waste a lot of energy as heat. This means that they consume more electricity and have a higher operating cost compared to more modern lighting technologies.
- Short lifespan: Carbon filament bulbs have a relatively short lifespan compared to other types of bulbs, typically lasting between 1,000 and 2,000 hours. This means that they need to be replaced more frequently, which can be inconvenient and costly.
- Fragility: Carbon filament bulbs are quite fragile and can break easily if dropped or bumped. This makes them less suitable for use in high-traffic areas or in locations where they may be exposed to vibration or movement.
- Limited brightness: Carbon filament bulbs are typically not as bright as other types of bulbs, which means that they may not provide enough light for certain applications. They are best used for decorative or accent lighting, rather than for general illumination.
- Heat generation: Carbon filament bulbs generate a lot of heat, which can be a concern in certain applications. For example, they may not be suitable for use in enclosed fixtures or in locations where heat buildup can be a problem.
- Environmental impact: While carbon filament bulbs do not contain hazardous materials like mercury, they are not as environmentally friendly as newer lighting technologies like LED bulbs. They consume more energy and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, which can have negative impacts on the environment.
- Limited availability: Carbon filament bulbs may be less widely available compared to other types of bulbs, as they are not as commonly used or manufactured today. This can make them more difficult to find or more expensive to purchase.
Carbon arc light bulbs
Carbon arc light bulbs are a type of electric lamp that uses a pair of carbon electrodes to produce a bright, intense light. They were first developed in the 1800s and were widely used for outdoor lighting and in early film projectors.
The carbon arc bulb consists of two carbon rods, called electrodes, that are positioned parallel to each other and slightly separated. When an electric current is passed through the electrodes, they become very hot and create an arc of light between them.
The carbon arc produces a bright, intense light that is ideal for outdoor lighting and for illuminating large areas, such as theaters and sports stadiums. However, carbon arc bulbs have several disadvantages, including a short lifespan, high heat generation, and the need for frequent maintenance.
In order to keep the electrodes from burning up, a mechanism is typically used to keep them separated and to automatically adjust the distance between them as they wear down. The mechanism is known as a "feed mechanism" and is usually powered by a motor or other type of mechanism.
Carbon arc bulbs also require a large amount of electrical power and generate a lot of heat, which can be a concern in certain applications. They are not typically used in modern lighting applications due to their inefficiency and high maintenance requirements.
Advantages:
- Intense light: Carbon arc bulbs produce a bright, intense light that is ideal for outdoor lighting, industrial applications, and large-scale projection systems.
- High color temperature: Carbon arc bulbs produce a light with a high color temperature, which is often preferred for certain types of photography and film projection.
- Long-distance projection: Carbon arc bulbs are able to project light over long distances, making them suitable for large-scale outdoor lighting and projection applications.
- High efficacy: Carbon arc bulbs have a relatively high efficacy, which means that they produce a lot of light for the amount of energy they consume.
- High CRI: Carbon arc bulbs typically have a high color rendering index (CRI), which means that they are able to accurately reproduce colors in a way that is pleasing to the eye.
- Compatibility with existing equipment: Carbon arc bulbs are compatible with many existing projection and lighting systems, which means that they can often be easily integrated into existing setups.
- Low cost: Carbon arc bulbs can be relatively inexpensive compared to other types of high-intensity lighting technologies, making them an affordable option for certain applications.
- Short warm-up time: Carbon arc bulbs light up quickly, without the need for a long warm-up time.
- Historic value: Carbon arc bulbs have a long history and are associated with early film projection and outdoor lighting, which can add a sense of nostalgia or historical interest to certain applications.
Disadvantages:
- Short lifespan: Carbon arc bulbs have a relatively short lifespan, typically lasting only a few hundred hours before the electrodes need to be replaced. This can result in higher maintenance costs and downtime for equipment.
- High heat generation: Carbon arc bulbs produce a significant amount of heat, which can be a concern in certain applications. They may require additional cooling systems to prevent overheating and damage to surrounding equipment.
- Fragility: The carbon electrodes in carbon arc bulbs are quite fragile and can be easily damaged or broken, which can result in the need for frequent replacement.
- Safety concerns: Carbon arc bulbs can pose safety hazards due to the high temperatures and potential for sparking or arcing. They require specialized equipment and safety precautions to operate safely.
- High energy consumption: Carbon arc bulbs require a large amount of energy to operate, which can result in higher electricity bills and energy costs.
- Environmental impact: Carbon arc bulbs are not as environmentally friendly as newer lighting technologies, as they consume more energy and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Limited applications: Carbon arc bulbs are not suitable for all applications due to their high heat generation, fragility, and short lifespan. They are primarily used in specialized applications such as outdoor lighting and industrial equipment.
- Availability: Carbon arc bulbs are not as widely available as other types of bulbs, and may require specialized suppliers or equipment to obtain.